Gynecomastia Surgery in Boston, MA and Providence, RI
We may be able to help you!
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a condition that affects men of all ages, from infants to older adults. It's a benign enlargement of breast tissue in males that results in the development of breasts. The term "gynecomastia" comes from the Greek words "gyne" meaning woman and "mastos" meaning breast, describing the condition's feminine appearance.
While gynecomastia is not a life-threatening condition, it can cause emotional distress, making it essential to seek medical attention. The condition can resolve on its own, but some men may require treatment to alleviate symptoms.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is relatively common in newborn males, affecting up to 60% of infants due to the transfer of maternal estrogen during pregnancy. The condition usually resolves within a few weeks or months after birth, as the infant's hormone levels stabilize.
t should also be mentioned that the causes of gynecomastia can be hormonal changes, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. Here are some of the most common causes of gynecomastia:
- Hormonal changes: Gynecomastia is often caused by hormonal imbalances, specifically an increase in estrogen and a decrease in testosterone levels. This imbalance can occur during puberty, which is the most common time for gynecomastia to develop. Hormonal changes can also occur in older men, leading to the development of gynecomastia.
- Medications: Certain medications can cause gynecomastia as a side effect, including anabolic steroids, anti-androgens, and some medications used to treat ulcers and heart conditions.
- Diseases: Certain diseases can cause gynecomastia, such as hyperthyroidism, liver disease, and kidney failure. In some cases, cancer can also cause gynecomastia
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
- Enlarged breasts.
- Swollen breast gland tissue.
- Pain or tenderness.
Gynecomastia surgery procedure
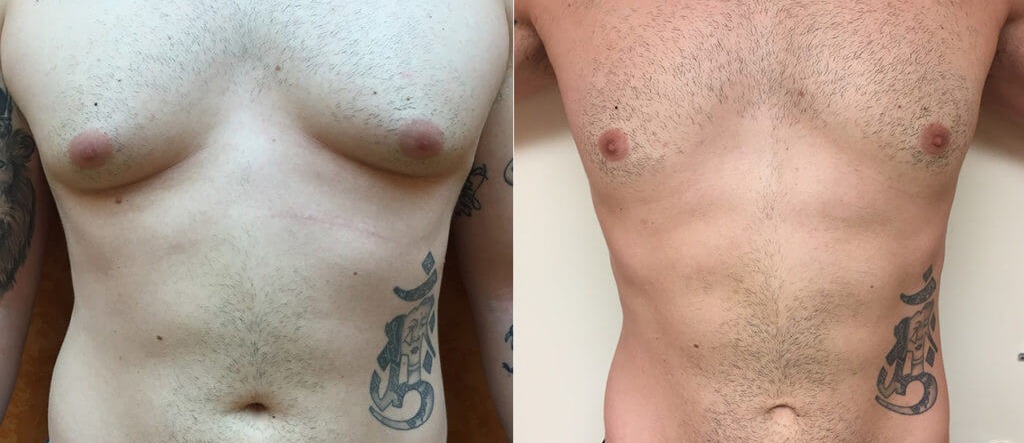
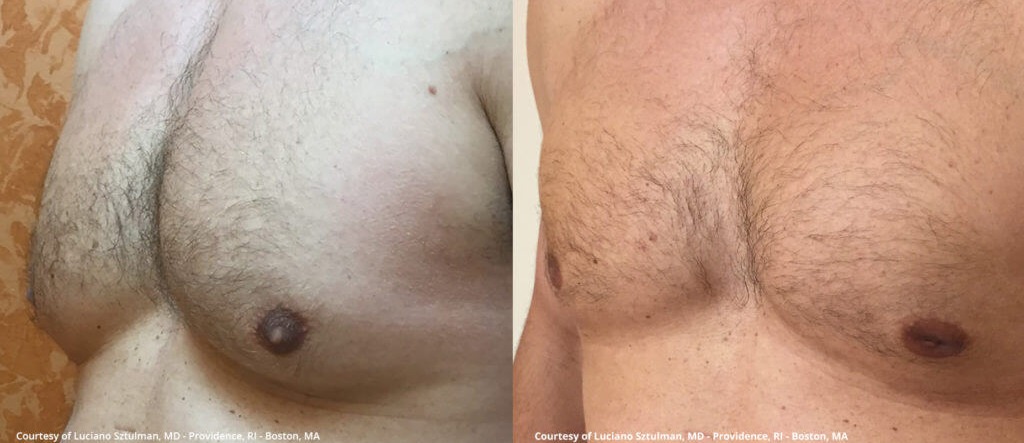
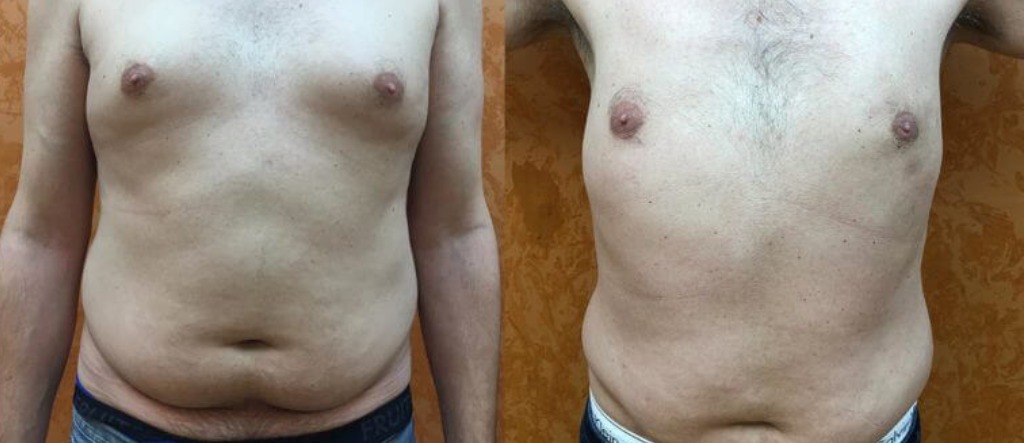
Gynecomastia surgery, also known as male breast reduction surgery, is typically performed on an outpatient basis and can be done under local anesthesia. The surgery can take anywhere from one to three hours, depending on the extent of the procedure.
The first step in the surgery is making incisions around the areola or nipple area to allow access to the breast tissue. The surgeon will then remove the excess glandular tissue, fat, and skin through these incisions, reshaping the chest into a more masculine contour. In cases where there is significant sagging of the breast tissue, the surgeon may also need to remove excess skin to achieve the desired result.
After the excess tissue and fat have been removed, the incisions are closed using sutures, and a compression garment is placed over the chest to reduce swelling and support the healing process. The patient will typically be able to go home on the same day as the surgery but will need to arrange for someone to drive them home.
Following the surgery, the patient may experience some discomfort, swelling, and bruising, which can be managed with pain medication and the use of ice packs. It is important to avoid strenuous activity and heavy lifting for several weeks after the surgery to allow for proper healing.
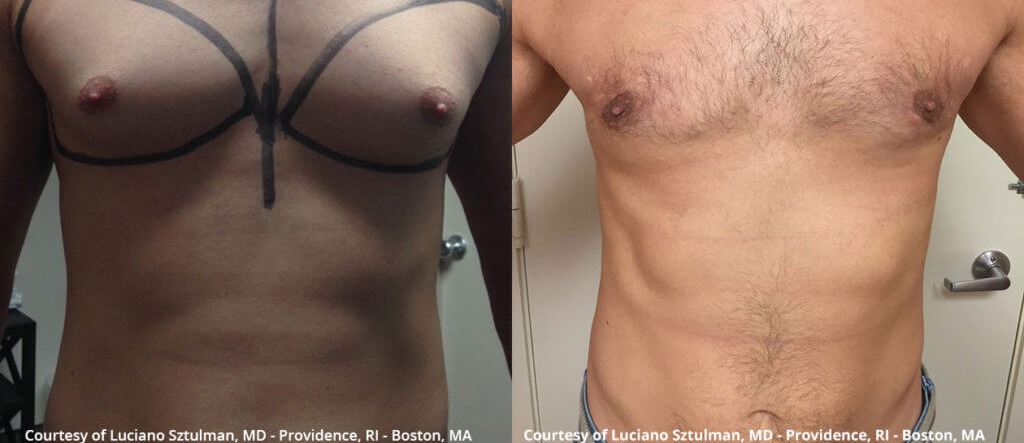
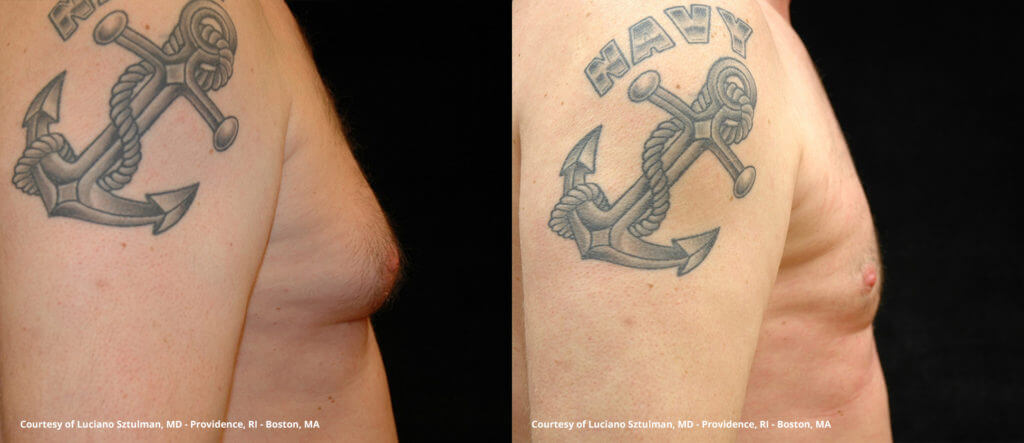
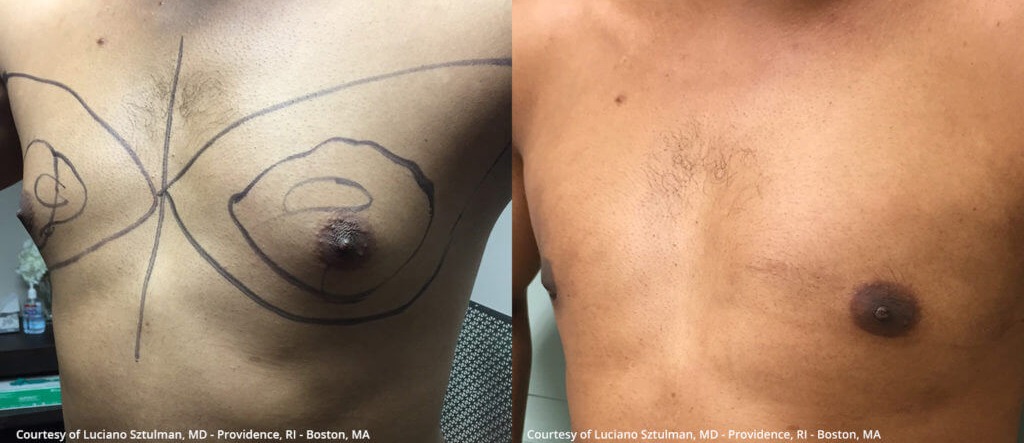
Gynecomastia surgery before and after
Gynecomastia surgery recovery
After the surgery, we will provide specific instructions on how to care for your incisions, how to manage any pain or discomfort, and when to return for follow-up appointments. Following these instructions closely is important to ensure the best possible outcome.
- Wear compression garments: You'll likely be instructed to wear a compression garment for several weeks after surgery to help reduce swelling and support the healing process.
- Take pain medication as prescribed: Pain medication to manage any discomfort after surgery. Take the medication as prescribed and don't exceed the recommended dosage.
- Avoid strenuous activity: It's important to avoid any strenuous activity or heavy lifting for at least a few weeks after surgery to give your body time to heal. Light exercise, such as walking, is usually fine after a few days, but consult with your surgeon for specific recommendations.
- Diet: Eating a healthy diet can help support the healing process and prevent complications. Make sure to eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean protein and to drink plenty of fluids
- Rest: Getting enough rest is crucial for a speedy recovery.
- Keep your incisions clean and dry: You'll get special instructions on how to care for your incisions, and avoid exposing them to water until they have fully healed.
Risks of gynecomastia surgery
Male breast reduction surgery is generally considered safe, but like any surgical procedure, it carries some risks.
- Bleeding and hematoma formation: Bleeding during or after surgery can cause hematoma formation, which is a collection of blood that can cause swelling and pain. In some cases, hematoma formation may require surgical drainage.
- Infection: Like any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection with gynecomastia surgery. Infections can cause fever, pain, and other symptoms and may require antibiotics or additional surgery to treat.
- Scarring: Gynecomastia surgery involves incisions in the breast area, which can lead to scarring. While the scars generally fade over time, some men may be left with visible scars.
- Changes in sensation: Gynecomastia surgery can damage nerves in the breast area, which can lead to changes in sensation. This can include numbness, tingling, or reduced sensation in the chest area.
- Asymmetry: There is a risk of asymmetry after gynecomastia surgery, with one breast appearing larger or shaped differently than the other.
- Anesthesia risks: Like any surgical procedure, gynecomastia surgery requires anesthesia, which carries its own risks. These risks include allergic reactions, respiratory problems, and other complications.
- Recurrence of breast tissue: In some cases, breast tissue may grow back after gynecomastia surgery, requiring additional treatment.